Time Deposit Account
What Is A Current Account?
The interest paid on a time deposit tends to be higher than on an at-call savings account, but tends to be lower than that of riskier products such as stocks or bonds. Some banks offer market-linked time deposit accounts which offer potentially higher returns while guaranteeing principal. Garanti 3 Month Time Deposit The rate applies for a three month term for the 'TL E-Time Deposit Account' that requires more than 500.000,00 TRY. USD and Euro foreign currency account time deposits are also available from this bank. TRY: 16.26%: Aug, 2019: 1 month: Ziraat Bankasi 1 Month Time Deposit. In fact, Marcus guarantees that you'll receive the highest rate it offers on a CD within 10 days of opening an account, as long as you deposit $500 during that time.
A current account is for use by sole proprietors, companies, partnerships, associations, trusts, etc. to make current transactions. All business transactions are conducted through a current account. A current account does not have an end or maturity date.
What Is A Deposit Account/Savings Account?

Time Deposit Account Withdrawal
A savings account is a basic deposit account for an individual to carry out day-to-day transactions and withdrawals. A deposit account can be held individually or jointly by two or more people. A savings account does not have an end or maturity date as well.
Difference Between Current Account And Deposit Account
Some of the differences between a current account and a deposit account are:
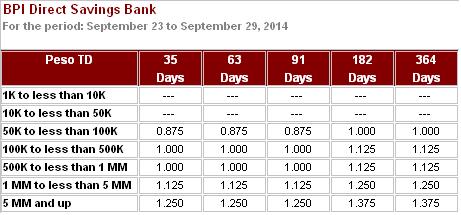
Time Deposit Account Types
- Interest
Interest applies to the minimum balance available in a deposit account. The interest is applicable on the minimum account balance, every day. Banks offer interest rates of 4% or more on savings accounts. Current accounts, on the other hand, are non-interest accounts. There is no interest for any balance in a current account. Although, this may change in the future.
- Transaction rates
Transaction rates apply for withdrawals made over the limit of free withdrawals (usually 3-5) made in deposit accounts. Thus, a savings account holder will have to pay the transaction rate applicable by the bank (eg: INR 20, 25, 50, 90, etc.). Conversely, there are no transaction rates applicable on current accounts. Businesses transact more than individuals and thus, there is no transaction rates or limits on current accounts.
- Minimum balance
Deposit account-holders must maintain a daily average minimum balance in their account. This amount varies from bank to bank and some banks even offer zero-balance deposit/savings accounts. In this case, current account-holders also must maintain a minimum balance in their bank accounts. The minimum balance required for a current account is much higher than the minimum balance required for deposit accounts.
- Overdraft facility
Time Deposit Account Interest Rates
Deposit account-holders can only withdraw what balance is in their saving account. Banks do not offer overdraft facilities on saving accounts unless the customer is a salaried account-holder (approved companies). Whereas, current account-holders can withdraw over and above the balance in an account. Overdraft facilities help businesses to make up cash flows when there is a shortage of funds. Interest is applicable to the overdraft amount taken.